Six Strategies: How to Reduce the Bullwhip Effect In Supply Chains

March 28, 2024
By: Brian Lindner
In an era where supply chain dynamics are increasingly volatile, the bullwhip effect emerges as a critical challenge for businesses striving for operational excellence. This phenomenon, where minor variations in consumer demand trigger significant fluctuations in upstream supply chain orders, mirrors the dramatic amplification seen in the crack of a whip. This analogy aptly illustrates how small changes can have disproportionate impacts, leading to inefficiencies, increased costs, and excess inventory. Through a deeper exploration of the causes and solutions to this pervasive issue, businesses can fortify their supply chains against this disruptive force.
Unraveling the Complexity of the Bullwhip Effect
The bullwhip effect underscores the interconnectedness and fragility of modern supply chains. There’s a great example of this dynamic within the automotive industry, where Volvo experienced an overabundance of green cars due to misinterpretation of demand signals by its manufacturing department. The Volvo sales team, aiming to clear the excess, developed a specialized program to sell off the surplus green cars. While their efforts were successful, and the inventory was reduced, the underlying issue was unresolved due to a critical breakdown in internal communication and demand forecasting. Such scenarios underscore the necessity for refined strategies to mitigate these disruptions.
Diving into the Causes of Bullwhip Effect
The origins of the bullwhip effect are multifaceted, involving:
- Order Batching: This practice often stems from a desire to streamline operations and reduce shipping costs, leading companies to place larger, less frequent orders. However, this can cause significant swings in inventory levels as suppliers ramp up production to meet these bulk orders, followed by periods of inactivity. While economically motivated, this batch system for placing orders, can obscure the accurate picture of demand, leading to a mismatch between supply and inventory levels.
- Price Fluctuations: Sales promotions and special discounts are common strategies to boost demand, but these temporary price changes can distort the demand signal received by upstream partners. Consumers may over-purchase in anticipation of future price increases or stock shortages, leading to a brief spike in demand that does not reflect long-term consumption patterns. When these distorted signals travel up the supply chain, they can result in overproduction, excess inventory, and increased holding costs.
- Communication Breakdowns: Without transparent and real-time communication, supply chain entities end up making decisions based on partial or outdated information. This lack of coordination can lead to significant discrepancies between production, inventory, and market demand. For instance, a retailer’s overestimation of demand can unnecessarily lead suppliers to increase production, only for the excess products to accumulate as unsold inventory.
- Lead Time Variability: The lag time between order placement and delivery can vary due to various factors, including manufacturing delays, transportation issues, and customs clearance times. This variability makes it challenging for companies to synchronize their supply chain activities with actual demand. When companies compensate for these uncertainties by ordering more than necessary, the bullwhip effect exacerbates stockpiles of unsold goods and wasted resources.
- Evolving Consumer Expectations: Today’s consumers demand variety, rapid delivery times, and flexible purchasing options. This has led companies to diversify their distribution channels and maintain higher inventory levels to meet these expectations. However, this complexity can strain the supply chain as companies struggle to forecast demand accurately across multiple channels, leading to either stockouts or overstock situations.
- Unexpected Disruptions: The global nature of modern supply chains exposes them to a wide range of disruptions, from natural disasters to geopolitical tensions. These events can suddenly alter supply chain dynamics, forcing companies to scramble to adjust their operations. The COVID-19 pandemic, for example, highlighted the vulnerabilities in global supply chains, as lockdowns and transportation restrictions led to widespread shortages and delays.
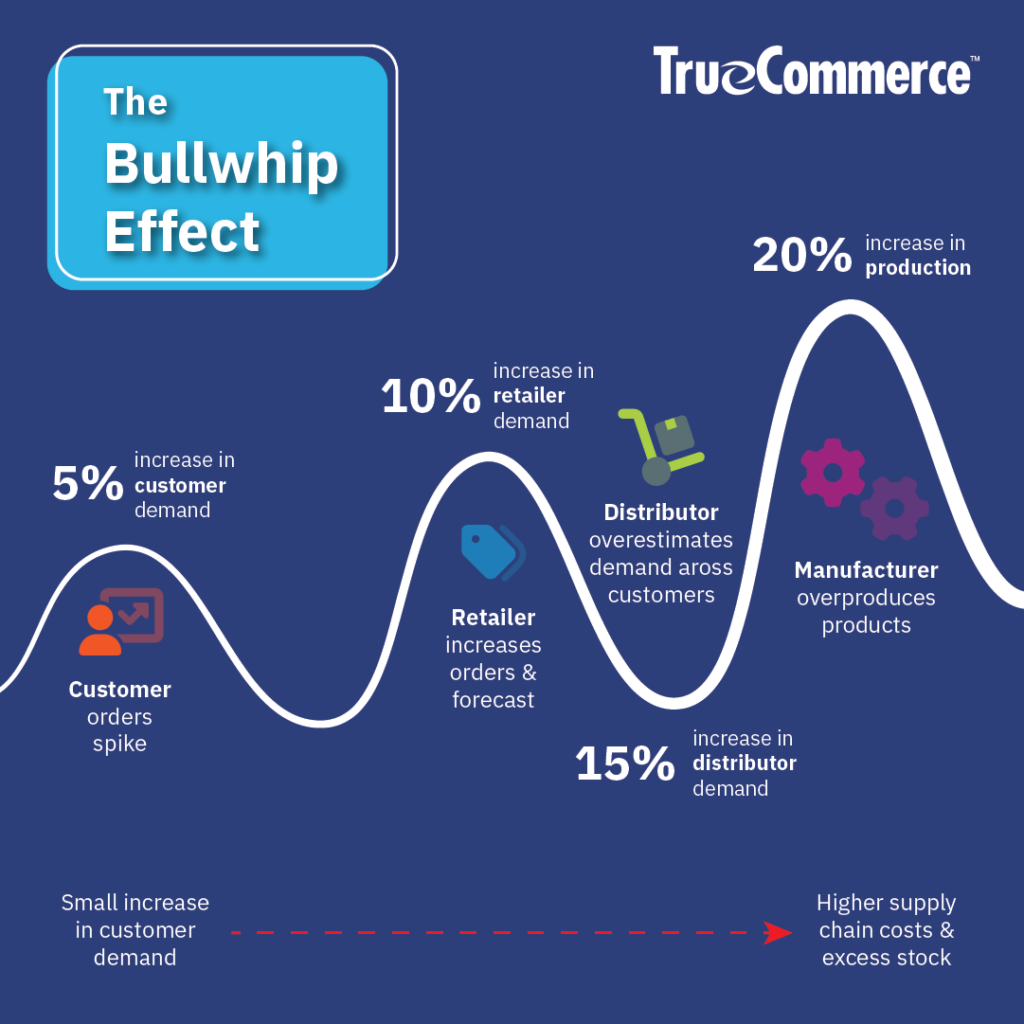
The Ripple Effect in Action
The interaction of these factors can create a vicious cycle where each stage of the supply chain amplifies the distortions of the previous one, much like the escalating waves of a whip. The initial misinterpretation of demand signals leads to progressively larger swings in order volume and inventory levels as one moves upstream in the supply chain. This undermines the supply chain’s efficiency and responsiveness, resulting in significant economic costs, including wasted resources, lost sales, and eroded customer trust.
Understanding the nature of the bullwhip effect is the first step toward developing targeted strategies to mitigate its impact. Businesses can enhance their supply chain resilience and adaptability by addressing each underlying cause, from improving communication and collaboration to adopting advanced forecasting and inventory management techniques. In doing so, they protect themselves against the immediate challenges of the bullwhip effect and lay the foundation for a more agile, responsive, and customer-centric supply chain.
Fortifying the Supply Chain: Strategies for Mitigation
Addressing the bullwhip effect requires a comprehensive approach to blending technology, collaboration, and strategic foresight. The following are six fundamental strategies for curating this comprehensive approach, each targeting key aspects of the bullwhip effect to foster a more synchronized and resilient supply chain.
1. Enhancing Supply Chain Visibility
The foundation of an effective response lies in achieving end-to-end visibility across the supply chain. Tools like Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) play pivotal roles in this context. EDI facilitates real-time communication and data exchange between supply chain partners, streamlining processes from ordering to invoicing. IoT technologies offer granular insights into inventory levels and product locations through sensors and connected devices, fostering transparency and enabling proactive management of potential disruptions.
2. Leveraging Predictive Analytics and AI
Advanced forecasting models, powered by predictive analytics and artificial intelligence (AI), offer a robust solution to anticipating demand fluctuations more accurately. These technologies can digest vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and predict future trends, enhancing decision-making and inventory management. Incorporating AI into demand forecasting reduces the likelihood of overstocking and aligns production more closely with actual market needs.
3. Fostering Collaborative Partnerships
The complexity of modern supply chains necessitates a collaborative approach, where supply chain partners share information and work together towards common goals. This collaboration extends beyond mere transactional interactions, enabling strategic alliances that enhance forecast accuracy, streamline replenishment processes, and build resilience against disruptions. Shared KPIs and performance metrics further align the efforts of all parties, ensuring a unified response to market dynamics.
4. Streamlining Ordering Practices
Addressing the issue of order batching requires a shift towards more consistent and predictable ordering practices. Engaging in dialogue with partners to understand and accommodate each other’s capabilities and constraints can lead to more synchronized supply chain operations. This approach minimizes surprises and enables smoother adjustments to inventory levels, reducing the risk of sudden spikes or drops in demand.
5. Adopting Agile Inventory Management
Agility in inventory management is crucial for navigating the uncertainties inherent in global supply chains. This proficiency entails flexible inventory strategies and the willingness to innovate and adapt to changing conditions. Techniques such as vendor managed inventory (VMI) and Just-in-Time (JIT) delivery can optimize stock levels and reduce lead times, making the supply chain more responsive to actual demand.
6. Navigating the Future of Supply Chain Management
As businesses grapple with the complexities of the bullwhip effect, the integration of technology, strategic collaboration, and agile practices emerge as the blueprint for resilience. By embracing these principles, companies can transform their supply chains into robust, adaptive networks capable of withstanding the pressures of an unpredictable global marketplace.
In conclusion, conquering the bullwhip effect is not just about mitigating risks; it’s about seizing the opportunity to revolutionize supply chain management. Businesses can achieve a competitive edge through concerted efforts to enhance visibility, embrace predictive technologies, cultivate collaboration. The journey toward supply chain excellence is continuous, demanding vigilance, innovation, and a commitment to strategic partnerships. In doing so, companies can not only navigate the challenges of today but also pave the way for a more efficient, resilient, and customer-centric supply chain future.
Author: Brian Lindner
Author Bio: Brian Lindner is the Director of Marketing Supply Chain Technology at TrueCommerce. He has spent the last 15 years in B2B project management and marketing. His focus is on Vendor Managed Inventory and related eCommerce solutions that help companies save time through automation. Brian enjoys spending time with his wife and 2 kids and in his spare time brews delicious craft beer with his friends.
Check out the IDC MarketScape: Worldwide Multi-Enterprise Supply Chain Network (MESCCN) 2023 Vendor Assessment where TrueCommerce is recognized as a Leader.
Share this post:
Stay ahead of the competition
Get expert supply chain insights delivered directly to your inbox weekly.